Page 250 - Shimadu Consumables Catalog
P. 250
Appendix I
Septa
Septa Selection Guide
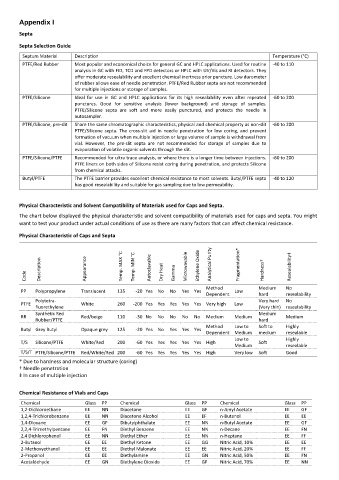
Septum Material Description Temperature (°C)
PTFE/Red Rubber Most popular and economical choice for general GC and HPLC applications. Used for routine -40 to 110
analysis in GC with FID, TCD and FPD detectors or HPLC with UV/Vis and RI detectors. They
offer moderate resealability and excellent chemical inertness prior puncture. Low durometer
of rubber allows ease of needle penetration. PTFE/Red Rubber septa are not recommended
for multiple injections or storage of samples.
PTFE/Silicone Ideal for use in GC and HPLC applications for its high resealability even after repeated -60 to 200
punctures. Good for sensitive analysis (lower background) and storage of samples.
PTFE/Silicone septa are soft and more easily punctured, and protects the needle in
autosampler.
PTFE/Silicone, pre-slit Share the same chromatographic characteristics, physical and chemical property as non-slit -60 to 200
PTFE/Silicone septa. The cross-slit aid in needle penetration for low coring, and prevent
formation of vacuum when multiple injection or large volume of sample is withdrawal from
vial. However, the pre-slit septa are not recommended for storage of samples due to
evaporation of volatile organic solvents through the slit.
PTFE/Silicone/PTFE Recommended for ultra trace analysis, or where there is a longer time between injections. -60 to 200
PTFE liners on both sides of Silicone resist coring during penetration, and protects Silicone
from chemical attacks.
Butyl/PTFE The PTFE barrier provides excellent chemical resistance to most solvents. Butyl/PTFE septa -40 to 120
has good resealability and suitable for gas sampling due to low permeability.
Physical Characteristic and Solvent Compatibility of Materials used for Caps and Septa.
The chart below displayed the physical characteristic and solvent compatibility of materials used for caps and septa. You might
want to test your product under actual conditions of use as there are many factors that can affect chemical resistance.
Physical Characteristic of Caps and Septa
Description Appearance Temp. MAX °C Temp. MIN °C Autoclavable Dry Heat Microwavable Ethylene Oxide Analytical Purity Fragmentation* Hardness† Resealability‡
Code Gamma
Method Medium No
PP Polypropylene Translucent 135 -20 Yes No No Yes Yes Low
Dependent hard resealability
Polytetra- Very hard No
PTFE White 260 -200 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Very high Low
fluorethylene (Very thin) resealability
Synthetic Red Medium
RR Red/beige 110 -30 No No No No No Medium Medium Medium
Rubber/PTFE hard
Method Low to Soft to Highly
Butyl Grey Butyl Opaque grey 125 -20 Yes No Yes Yes Yes
Dependent Medium medium resealable
Low to Highly
T/S Silicone/PTFE White/Red 200 -60 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes High Soft
Medium resealable
T/S/T PTFE/Silicone/PTFE Red/White/Red 200 -60 Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes High Very low Soft Good
* Due to hardness and molecular structure (coring)
† Needle penetration
‡ In case of multiple injection
Chemical Resistance of Vials and Caps
Chemical Glass PP Chemical Glass PP Chemical Glass PP
1,2-Dichloroethane EE NN Diacetone EE GF n-Amyl Acetate EE GF
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene EE NN Diacetone Alcohol EE EF n-Butanol EE EE
1,4-Dioxane EE GF Dibutylphthalate EE NN n-Butyl Acetate EE GF
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane EE FN Diethyl Benzene EE NN n-Decane EE FN
2,4 Dichlorophenol EE NN Diethyl Ether EE NN n-Heptane EE FF
2-Butanol EE EE Diethyl Ketone EE GG Nitric Acid, 10% EE EE
2-Methoxyethanol EE EE Diethyl Malonate EE EE Nitric Acid, 20% EE FF
2-Propanol EE EE Diethylamine EE GN Nitric Acid, 50% EE FN
Acetaldehyde EE GN Diethylene Dioxide EE GF Nitric Acid, 70% EE NN