Page 2 - Solutions for Contaminant Analysis
P. 2
Total Support for Contaminant Analysis and Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometers (EDX)
Failure Identi cation When a material is irradiated with X-rays, each element in the material generates unique X-rays (X-ray uorescence). The elements and the concentrations of those
elements in the material can be determined based on the energies of these X-rays and their intensity. EDX systems can analyze samples in various forms with no
The adulteration of products by contaminants causes a wide range of problems in every sector of industry. chemical pretreatment, including solid, liquid, and powder samples, and are ideal for contaminant analysis when preserving the sample is a priority.
These problems can only be resolved by analyzing the contaminating material and identifying its source.
Shimadzu offers a powerful range of products and tools for contaminant analysis and failure analysis.
˙ EDX-7200 / 8100
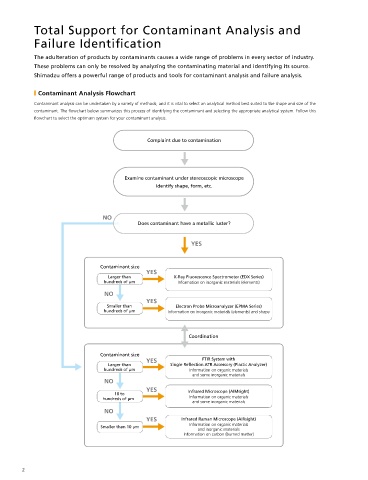
˙ Contaminant Analysis Flowchart These agship models in the Shimadzu EDX series are equipped with a liquid nitrogen-free, high-performance
semiconductor detector, a collimator, and sample camera effective for the analysis of very small samples and very small
Contaminant analysis can be undertaken by a variety of methods, and it is vital to select an analytical method best suited to the shape and size of the
sample quantities, and also support helium purge analysis and vacuum analysis (optional) for highly sensitive measure-
contaminant. The owchart below summarizes this process of identifying the contaminant and selecting the appropriate analytical system. Follow this
ment of light elements.
owchart to select the optimum system for your contaminant analysis.
EDX-7200 / 8100
˙ Analysis of a Microscopic Metal Contaminant on a Molded Plastic Product
EDX systems are non-destructive and can perform elemental analysis, thus are effective for analyzing contaminants that are mixed with or adhered to foods,
Complaint due to contamination
pharmaceuticals, and other products. The sample camera and collimator allow for easy characterization of very small contaminants, and the irradiation eld diameter
can be adjusted to match the sample size, reducing the in uence of the surrounding material. In the example below, these system features enabled quantitative data to
be accurately matched with reference data and the contaminant to be identi ed as SUS316 stainless steel.
Examine contaminant under stereoscopic microscope
Identify shape, form, etc.
Contaminant area
Normal area
NO
Does contaminant have a metallic luster? View of Sample EDX Pro les of Contaminant Area (Red)
and Normal Area (Blue) Superimposed
YES
Contaminant size
YES Results from Quantitative Analysis of
Larger than X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (EDX Series) Contaminant by FP Method
hundreds of µm Information on inorganic materials (elements) Titanium (Ti) and Zinc (Zn) were detected in the material
around the contaminant and excluded from quantitative Results of Data Matching
NO calculations. (Collected data was compared against an internal library,
YES identifying the contaminant as SUS316)
Smaller than Electron Probe Microanalyzer (EPMA Series)
hundreds of µm Information on inorganic materials (elements) and shape ˙ A Metal Particle (Approx. 0.1 mm Diameter) Attached to a Piece of Confectionery
A metal particle approx. 0.1 mm in diameter was attached to a piece of confectionery and analyzed with irradiation eld diameters of 1 mm and 0.3 mm. The 1 mm
eld diameter resulted in a larger overall background effect due to irradiation scatter from the area surrounding the metal particle (from the confectionery) and a
Coordination poorer S/N ratio, while the 0.3 mm eld diameter reduced the X-rays scattered by the surrounding area and produced in an EDX pro le with a good S/N ratio. Copper
(Cu) and zinc (Zn) were the main components detected at both irradiation eld diameters and the metal particle was identi ed as brass at both irradiation eld sizes,
but the 0.3 mm eld size also detected a lead (Pb) peak, which suggested the metal particle was free cutting brass. This shows the smaller irradiation eld diameter of
Contaminant size 0.3 mm offers a more accurate analysis of small contaminants surrounded by organic and other materials that generate large amounts of scattered X-rays.
YES FTIR System with
Larger than Single Re ection ATR Accessory (Plastic Analyzer) CuKa
hundreds of µm Information on organic materials П1 mm RhKaC
and some inorganic materials П0.3 mm
NO CaKa ZnKa
YES ZnKb
10 to Infrared Microscope (AIMsight) Image of Sample
hundreds of µm Information on organic materials (Middle yellow circle is
and some inorganic materials PbLa PbLb1 0.3 mm in diameter)
NO CuKb RhKa
YES Infrared Raman Microscope (AIRsight) CaKb FeKa ZnKb SrKa RhKbC
Smaller than 10 µm Information on organic materials RhKb
and inorganic materials KKa PbLa PbLb1
Information on carbon (burned matter)
2 3