Page 8 - Food&Beverages PFAS_analysis
P. 8
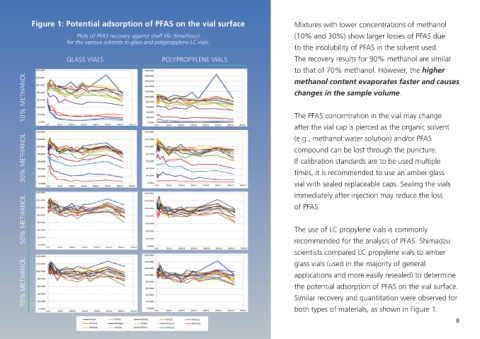
Figure 1: Potential adsorption of PFAS on the vial surface Mixtures with lower concentrations of methanol
Plots of PFAS recovery against shelf life (time/hour) (10% and 30%) show larger losses of PFAS due
for the various solvents in glass and polypropylene LC vials.
to the insolubility of PFAS in the solvent used.
GLASS VIALS POLYPROPYLENE VIALS The recovery results for 90% methanol are similar
to that of 70% methanol. However, the higher
10% METHANOL changes in the sample volume.
methanol content evaporates faster and causes
The PFAS concentration in the vial may change
after the vial cap is pierced as the organic solvent
30% METHANOL compound can be lost through the puncture.
(e.g., methanol:water solution) and/or PFAS
If calibration standards are to be used multiple
times, it is recommended to use an amber glass
vial with sealed replaceable caps. Sealing the vials
immediately after injection may reduce the loss
50% METHANOL The use of LC propylene vials is commonly
of PFAS.
recommended for the analysis of PFAS. Shimadzu
scientists compared LC propylene vials to amber
70% METHANOL applications and more easily resealed) to determine
glass vials (used in the majority of general
the potential adsorption of PFAS on the vial surface.
Similar recovery and quantitation were observed for
both types of materials, as shown in Figure 1.
8