Page 42 - Automotive Solution for Automotive
P. 42
Failure analysis and material control
Multifaceted Evaluation of Plastic Degradation RoHS Directive Compliant Screening System for Phthalate Esters
– Identifying Causes of Degradation and Understanding Effects of Degradation – – Contributing to the More Rapid Inspection of Materials and Parts –
Plastic properties can change or degrade not only due to heat, various organic solvents, or acidic or alkaline solutions, but also due to UV rays. In The use of phthalate esters is currently restricted in toys, food packaging, and other applications and there are even plans to regulate them as a
particular, if plastics are used outdoors (as automotive exterior parts, for example), they require UV resistance. Developing plastics resistant to UV restricted substance under the Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (RoHS
degradation requires understanding the causes and effects of the degradation. A deeper understanding can be determined from multifaceted Directive) in Europe. Even though transportation equipment is not governed by the RoHS Directive, due to the various industries involved in
evaluations. As an example of multifaceted degradation evaluation, ABS resin pellets were irradiated with UV rays and then changes in the mechanical reducing the use of the regulated substances, the automotive industry cannot ignore this trend.
properties at the resin surface were evaluated. An FTIR system was used to measure an infrared spectrum to evaluate macromolecular structural changes The Py-Screener phthalate ester screening system is able to significantly reduce the time and cost of analysis and is easy to operate even for
and a dynamic ultra micro hardness tester was used to measure the hardness of the resin surface. first-time users.
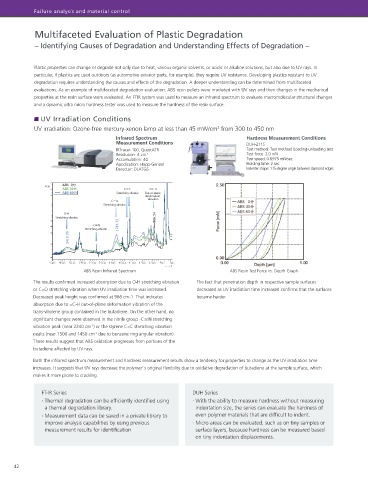
UV Irradiation Conditions Screening System for Phthalate Esters
UV irradiation: Ozone-free mercury-xenon lamp at less than 45 mW/cm from 300 to 450 nm
2
System allows even first-time users to screen samples easily.
Infrared Spectrum Hardness Measurement Conditions
Measurement Conditions DUH-211S Py-Screener
IRTracer-100, QuestATR Test method: Test method: Loading-unloading test — Making the Complicated Simple
Resolution: 4 cm -1 Test force: 2.0 mN
Accumulation: 40 Test speed: 0.0975 mN/sec
Apodization: Happ-Genzel Holding time: 2 sec
Detector: DLATGS Indenter shape: 115-degree angle between diamond edges
Py-GC/MS-specific standard
phthalate ester sample
(jointly developed with SGS Japan) Sampling toolkit
C=C =C-H
Stretching vibratio Out-of-plane
deformation
C=O vibration
Stretching vibratio
O-H
Stretching vibratio
-C≡N
Stretching vibratio
Includes everything required for sample preparation
ABS Resin Infrared Spectrum ABS Resin Test Force vs. Depth Graph
Sample preparation navigator Pass/fail results visible at a glance
The results confirmed increased absorption due to O-H stretching vibration The fact that penetration depth in respective sample surfaces
or C=O stretching vibration when UV irradiation time was increased. decreased as UV irradiation time increased confirms that the surfaces
Decreased peak height was confirmed at 966 cm-1. That indicates became harder.
absorption due to =C-H out-of-plane deformation vibration of the
trans-vinylene group contained in the butadiene. On the other hand, no
significant changes were observed in the nitrile group -C≡N stretching
vibration peak (near 2240 cm ) or the styrene C=C stretching vibration Measures samples easily by simply Navigator ensures reliable
-1
peaks (near 1500 and 1450 cm due to benzene ring angular vibration). entering sample information maintenance
-1
< Maintenance Navigator >
Click a picture or description to view each item.
These results suggest that ABS oxidation progresses from portions of the
butadiene affected by UV rays.
Both the infrared spectrum measurement and hardness measurement results show a tendency for properties to change as the UV irradiation time
increases. It suggests that UV rays decrease the polymer’s original flexibility due to oxidative degradation of butadiene at the sample surface, which Measures to take when List of consumables and
gas leak has occurred
replacement criteria
makes it more prone to cracking.
Dedicated software navigates necessary operations
FT-IR Series DUH Series
· Thermal degradation can be efficiently identified using · With the ability to measure hardness without measuring
a thermal degradation library. indentation size, the series can evaluate the hardness of · System does not require any organic solvents for sample preparation, reduces time and costs, and enables anyone to
· Measurement data can be saved in a private library to even polymer materials that are difficult to indent. perform rapid screening easily.
improve analysis capabilities by using previous · Micro areas can be evaluated, such as on tiny samples or
measurement results for identification. surface layers, because hardness can be measured based
on tiny indentation displacements.
42 43