Page 13 - Shimadzu Journal vol.5 Issue1
P. 13
Neuroscience
These studies, illustrate potential future directions to investigate the Where do we go from here?
dynamic relationships between interacting human brains using fNIRS Functional NIRS is a rapidly growing neuroimaging technology that
and hyperscanning techniques. Additionally, the language has doubled the number of publications every 3.5 years over the
hyperscanning studies document that well-known functional neural
anatomy such as the components of the language system are past 20 years (Boas et al., 2014), and the current trajectory is
observable using fNIRS, and that the additional features of exponential. The major development areas include instrumentation,
analysis methods, and optimization of experimental procedures for
cross-brain coherence and synchrony between two individuals can be
investigated as novel probes to characterize uncharted questions applications in mainstream areas of conventional neuroscience
that underlie the neural events of social interaction. These studies including neuro-development, perception and cognition, motor
control, and psychiatric and neurological disorders and treatments.
also confirm the advantages of technology that populates the Recent applications for neurofeedback (Lapborisuth, et al, 2017) and
surface of the head with full head coverage (Zhang, et al, 2016:
Zhang, et al, 2017; Dravida, et al, 2017). Since neural systems adult cognitive neuroscience of conflict (Noah, et al, 2017) illustrate
these new directories.However, the primary advantages of fNIRS are
depend upon signal cooperation between multiple areas (the related to signal acquisitions in natural environments not constrained
integration principle) the most successful NIRS technology will
depend upon sampling brain function over the entire brain. Potential by the limitations of a high magnetic field and uncomfortable
benefits include a landmark breakthrough in methodology and imaging conditions that restrict head motion and communication.
These advantages position fNIRS as a potential leading technology
technology leading to principles of neural organization engaged for a new frontier in neuroscience that aims to understand the
during interpersonal and reciprocal interactions. Future studies may
apply these new techniques to further understand the neural neural correlates of social behavior and cross-brain interpersonal
interactions (Pinti et al., 2015; Noah et al., 2015; Hirsch et al, 2017).
underpinnings of disorders of communication as well as how the Most of the pieces are in place for the realization of this major
neural underpinnings of social disability in developmental disorders
deviate from typical development. advance. The key development priorities toward this specific end
goal include: 1) computational algorithms focused on signal
components that represent the neural contributions of the signal
separate from systemic and other non-neural components (Kirilina et
al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2016); 2) full head coverage of optodes to
acquire the dynamic activity of underlying long-range neural circuits;
and 3) multimodal systems that synchronize combined acquisitions
of EEG, fNIRS, and eye-tracking measurements (for example) for a
comprehensive report of long-range brain mechanisms. The
co-occurrence of the BRAIN initiative and the emergence of fNIRS as
a mainstream neurotechnology catalyzes the impactful potential to
probe untapped neural systems specialized for interpersonal
interactions between two or more individuals.
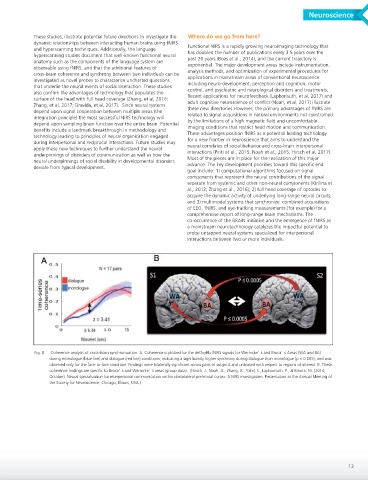
Fig. 8 Coherence analysis of cross-brain synchronization. A. Coherence is plotted for the deOxyHb fNIRS signals for Wernicke’ s and Broca’ s Areas (WA and BA)
during monologue (blue line) and dialogue (red line) conditions, indicating a significantly higher synchrony during dialogue than monologue (p < 0.005), and was
observed only for the face-to-face condition. Findings were bilaterally significant across pairs of subjects and unbiased with respect to regions of interest. B. These
coherence findings are specific to Broca’ s and Wernicke’ s areas (group data). (Hirsch, J., Noah, A., Zhang, X., Yahil, S., Lapborisuth, P., & Biriotti, M. (2014,
October). Neural specialization for interpersonal communication within dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: A NIRS investigation. Presentation at the Annual Meeting of
the Society for Neuroscience, Chicago, Illinois, USA.)
13