Page 7 - Shimadzu TOC-4200
P. 7
Diverse Applications
Measurement speed is the key feature of combustion catalytic oxidation TOC analyzers.
This characteristic can be exploited to support a diverse range of applications.
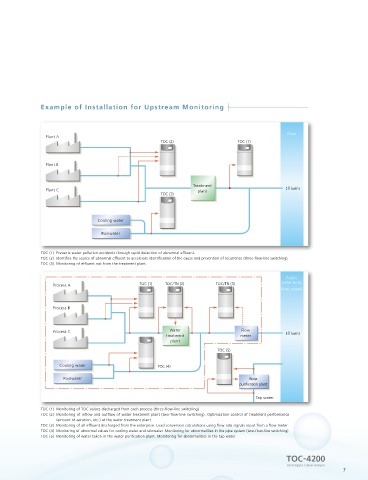
˙ Wastewater treatment plant influent (upstream monitoring) and effluent Example of Installation for Upstream Monitoring
• Measurements at a short measuring cycle (4 minutes minimum) rapidly capture
dramatic changes in organic matter or abnormal effluent.
River
• The powerful oxidation capacity of a combustion-type analyzer can detect organic Plant A
TOC (2) TOC (1)
matter that cannot be captured using a UV meter.
• The short measuring cycle and powerful oxidation, combined with switching between
up to six flow lines, offer detailed monitoring of treatment plants. Plant B
˙ Monitoring of river water sampled at water purification plants and Plant C Treatment Effluent
TOC (3) plant
treated water (tap water)
• Monitoring changes in river water quality due to rainfall and other factors to provide
control indicators for the treatment processes Cooling water
• Permits simultaneous monitoring of treated tap water.
Rainwater
˙ Supports monitoring TOC removal rate based on EPA Regulations. TOC (1) Prevents water pollution accidents through rapid detection of abnormal effluent.
TOC (2) Identifies the source of abnormal effluent to accelerate identification of the cause and prevention of recurrence (three-flow-line switching).
• Calculates TOC removal rate based on the U.S.A EPA regulations (Part IV 40 CFR Part 9, TOC (3) Monitoring of effluent not from the treatment plant
141 and 142, 1998). (*1)
Public
Process A TOC (1) TOC/TN (2) TOC/TN (3) water body
(river, ocean)
˙ Total pollutant load control regulation applications (organic pollution load)
• Converting the measured TOC values allows applications to COD total volume control. (*2) Process B
TOC → COD conversion functions are installed as standard.
• Reading flow rate signals from a flow meter (*1) permits COD load conversion calculations.
Process C Water Flow Effluent
treatment meter
plant
˙ Plant water TOC (5)
(washing water, cooling water, recovered water, boiler water, condensate,
Cooling water TOC (4)
etc.)
Rainwater Water
• Continuous monitoring of water used in a plant
purification plant
• Continuous monitoring of pure boiler water assists in the detection of anomalies, such
Tap water
as damaged pipes.
• The short measuring cycle (4 minutes minimum) of the combustion-type TOC analyzer TOC (1) Monitoring of TOC values discharged from each process (three-flow-line switching)
TOC (2) Monitoring of inflow and outflow of water treatment plant (two-flow-line switching). Optimization control of treatment performance
achieves more rapid detection of anomalies. (amount of aeration, etc.) at the water treatment plant
TOC (3) Monitoring of all effluent discharged from the enterprise. Load conversion calculations using flow rate signals input from a flow meter
TOC (4) Monitoring of abnormal values for cooling water and rainwater. Monitoring for abnormalities in the pipe system (two-flow-line switching)
TOC (5) Monitoring of water taken in the water purification plant. Monitoring for abnormalities in the tap water
*1 Optional
*2 The TOC-COD conversion formula must be determined separately.
TOC-4200
Total Organic Carbon Analyzer
6 7