Page 18 - Shimadzu SALD-2300
P. 18
Particle Size Analyzer Applications Measurement Technology Laser Diffraction Method
Particle size distribution is one of the main factors determining the characteristics of powders and particles. ・ There is a one-to-one correspondence between the particle diameter and the light intensity distribution pattern.
Powders and particles are used in a wide variety of fields for a wide range of objectives and applications. In some cases, they are used When a particle is irradiated with a laser beam, light is Scattered light 5.0 µm
directly as pharmaceuticals, catalysts, additives, or binders while in other situations they are used as raw ingredients. In either case, the emitted from the particle in every direction. This is (Side)
particle size distribution can have a major effect on the characteristics desired for a given application or objective, or on the performance “scattered light”. The intensity of the scattered light Scattering angle
and quality of a final product. Consequently, measuring the particle size distribution is essential for stabilizing or improving the varies with the scattering angle and describes a spatial (Back) Laser light (Forward)
characteristics, performance, or quality of powders or particles. intensity distribution pattern. This is a “light intensity Particle 2.0 µm
nm µm mm distribution pattern”. If the particle diameter is large, (Side)
nanometers micrometers millimeters
the scattered light emitted from the particle is Diffraction/Scattering by Particle
10 50 100 500 1 5 10 50 100 500 1 5 1.0 µm
concentrated in the forward direction (i.e., the direction of the laser beam), and fluctuates intensely in an
Liposomes angular range too small to be represented in a diagram. Compared to the light emitted in the forward direction,
Acetaminophens Pharmaceuticals the intensity of all other light is extremely low. As the particle diameter becomes smaller, the pattern of the
Titanium Oxide scattered light spreads outwards. As the particle becomes even smaller, the intensity of the light emitted to the 0.5 µm
Talc Cosmetics side and backwards becomes higher. The light intensity distribution pattern becomes gourd-shaped and spreads
Pearl Pigments
out in every direction. In this way, then, there is exists a one-to-one correspondence between the particle
Cornstarch 0.3 µm
Wheat Flour (cake flour) Food Products diameter and the light intensity distribution pattern. This means that the particle diameter can be ascertained by
detecting the light intensity distribution pattern.
Wheat Flour (bread flour)
Kaolinite
Alumina Ceramics ・ Measurement is performed on particle groups. 0.2 µm
Particle size distribution measurement is not performed on individual particles, but rather on particle groups
PVC Powder
Macromolecules
Acrylic Polymer Beads made up of large numbers of particles. Particle groups contain particles of different sizes, and the light intensity
Catalysts Vanadium Oxide distribution pattern emitted by a group is composed of all the scattered light emitted from all the individual 0.1 µm
particles. The particle size distribution, in other words, what particle sizes are present in what proportions, can
Zinc Sulfide
Electronic Materials
Phosphor be obtained by detecting and analyzing this light intensity distribution pattern. This is the basic principle behind
Clay Silt Sand
the laser diffraction method used in laser diffraction particle size analyzers. Correspondence between the
Soil and Civil Engineering Materials particle diameter and the light
Cement intensity distribution pattern.
・ Optical System in SALD-2300
0.01 0.05 0.1 0.5 1 5 10 50 100 500 1000 5000 The laser beam emitted from the light source (semiconductor laser) is Condensing lens Sensor for scattered light in the
forward area (Wing Sensor)
Particle Size: µm
converted into a thick beam with a collimator and this is directed at the
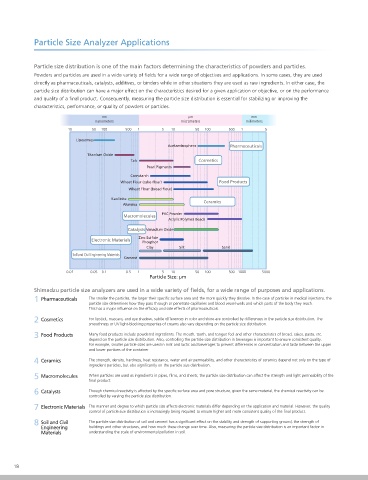
Shimadzu particle size analyzers are used in a wide variety of fields, for a wide range of purposes and applications. particle group. The scattered light emitted from the group in a forward Particles
1 Pharmaceuticals The smaller the particles, the larger their specific surface area and the more quickly they dissolve. In the case of particles in medical injections, the direction is concentrated with a lens, and concentric scattering images are
particle size determines how they pass through or penetrate capillaries and blood vessel walls and which parts of the body they reach. formed at a detecting plane positioned at a distance equal to the focal length.
This has a major influence on the efficacy and side effects of pharmaceuticals. Semiconductor laser Diffracted, scattered image
This is detected with the wing sensor in which light-receiving elements are Scattered light
2 Cosmetics For lipstick, mascara, and eye shadow, subtle differences in color and shine are controlled by differences in the particle size distribution. The arranged concentrically. The scattered light emitted to the side and backwards
smoothness or UV light-blocking properties of creams also vary depending on the particle size distribution.
is detected with side and back scattered light sensors. The light intensity
3 Food Products Many food products include powdered ingredients. The mouth, tooth, and tongue feel and other characteristics of bread, cakes, pasta, etc. distribution data can be obtained by detecting scattered light data of all Collimator lens Sensor for scattered light in side and backward areas
depend on the particle size distribution. Also, controlling the particle size distribution in beverages is important to ensure consistent quality.
For example, smaller particle sizes are used in milk and lactic acid beverages to prevent differences in concentration and taste between the upper directions. Sensor for backward scattered light
and lower portions of the container
Sensor for side scattered light
4 Ceramics The strength, density, hardness, heat resistance, water and air permeability, and other characteristics of ceramics depend not only on the type of ・ Flow of Light Intensity Detection and Data Processing 2.0µm Detection Wing Sensor II
ingredient particles, but also significantly on the particle size distribution.
With the SALD-2300 laser diffraction particle size analyzer, particle size Light intensity
5 Macromolecules When particles are used as ingredients in pipes, films, and sheets, the particle size distribution can affect the strength and light permeability of the distributions are calculated using light intensity distribution data. distribution pattern
final product.
The overall flow of detection and data processing is shown in the diagram to (%) 100
6 Catalysts Though chemical reactivity is affected by the specific surface area and pore structure, given the same material, the chemical reactivity can be the left. In measurement, the whole range of operations from the detection of 80
Light intensity
controlled by varying the particle size distribution. distribution data Light Intensity 60 40
scattered light intensity distribution patterns to the calculation of the particle 20
7 Electronic Materials The manner and degree to which particle size affects electronic materials differ depending on the application and material. However, the quality size distribution is executed as one process, and the particle size distribution 0
35
40
25
30
control of particle size distribution is increasingly being required to ensure higher and more consistent quality of the final product. 5 10 15 20 Sensor Element Number 45 50 55 60 65 5
data is output. Calculation of particle 3 (%) q 3 (%)
size distribution
8 Soil and Civil The particle size distribution of soil and cement has a significant effect on the stability and strength of supporting ground, the strength of Recalculation of particle size distributions can be performed by using the 100 90 80 50 40
Engineering buildings and other structures, and how much these change over time. Also, measuring the particle size distribution is an important factor in 70 60 30
Materials understanding the scale of environmental pollution in soil. previously detected and saved light intensity distribution data and selecting a Normalized Particle Amount Q 50 40 30 20
Particle size
refractive index that is different from the time of measurement. distribution data 20 10 0 10 0
0.01
5
0.050.1
0.5 1
Particle Diameter(µm) 10 50 100 500 1000
SALD-2300
18 Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analyzer 19