Page 5 - Shimadzu Nexera UC - Nexera UC Prep
P. 5
Analysis
Unified speed of analysis, sensitivity, and resolution
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a separation method that uses supercritical CO2 as the mobile phase.
The benefits of supercritical CO2 are the low polarity similar to n-hexane, the lower viscosity, and the high
diffusion coefficient, which offers potential advanced separation methods that are different from conventional
HPLC separation. Thanks to this feature, SFC enables unique analyses, such as high resolution chromatography,
simultaneous analysis of compounds over a wide polarity range, and improvement of MS detection sensitivity.
Very fast separation speed due to the relatively low viscosity of supercritical CO2
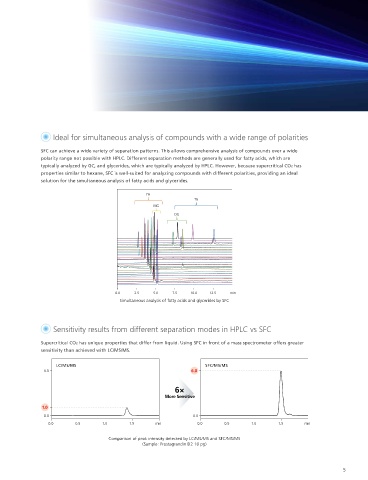
Ideal for simultaneous analysis of compounds with a wide range of polarities
Improved peak capacity and chromatographic resolution
Efficient separation of analogues and/or chiral compounds by high penetration mobile phase SFC can achieve a wide variety of separation patterns. This allows comprehensive analysis of compounds over a wide
polarity range not possible with HPLC. Different separation methods are generally used for fatty acids, which are
Different separation mode leads to high sensitivity
typically analyzed by GC, and glycerides, which are typically analyzed by HPLC. However, because supercritical CO2 has
properties similar to hexane, SFC is well-suited for analyzing compounds with different polarities, providing an ideal
solution for the simultaneous analysis of fatty acids and glycerides.
FA
TG
Higher resolution MG
DG
Improved separation and detection capabilities result from the low viscosity and high diffusion coefficient of
supercritical CO2. As shown below, Nexera UC demonstrates high-separation selectivity for isomeric compounds
that are difficult to separate by conventional HPLC.
Rs = 1.328
HPLC
0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 min
Simultaneous analysis of fatty acids and glycerides by SFC
0 4 8 12 min
Approx. 1/3 Sensitivity results from different separation modes in HPLC vs SFC
Supercritical CO2 has unique properties that differ from liquid. Using SFC in front of a mass spectrometer offers greater
sensitivity than achieved with LC/MS/MS.
SFC
Rs = 1.703 LC/MS/MS SFC/MS/MS
6.0 6.0
6×
More Sensitive
1.0
0.0 0.0
0 1 2 3 4 min 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 min 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 min
Comparison of separation acquired by Conventional HPLC and SFC Comparison of peak intensity detected by LC/MS/MS and SFC/MS/MS
(sample: α-tocopherol, column: Shim-pack UC-X Sil) (Sample: Prostagrandin D2 10 pg)
™
4 5