Page 4 - ELEM-Sport
P. 4
Spotting Targets Selectively
Hydrocarbon compounds are first separated by GC and then oxidatively dissociated in the element-selective combustion
unit. Then the separated compounds are detected by MS using the selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. As a result, the
difficult analysis of trace quantities of an oxygenated compound was enabled by using isotopic oxygen ( O2) as the y
18
oxidation gas (Pat. No. WO 2017/114654). Furthermore, nitrogen-containing compounds can be detected selectively by CxHyNzOw xCO2 + 2 H2O + zNO
using regular oxygen ( O2) as the oxidation gas.
16
If now-common CxHyNzOw hydrocarbons are directly detected by
m/z 44(CO2) FID or GC-MS after column separation, then they are detected
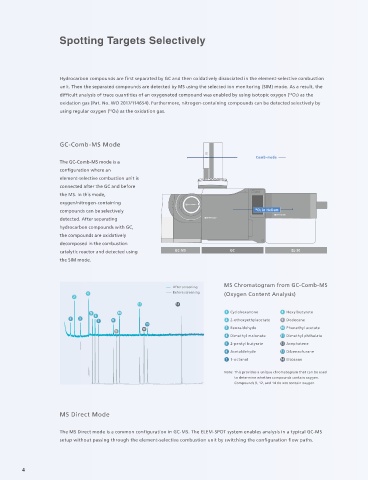
GC-Comb-MS Mode Oxidative based on a single peak. If that peak is detected by GC-MS after
dissociation m/z 18(H2O) column separation and oxidative dissociation, and further
Comb-mode
The GC-Comb-MS mode is a analyzed by m/z, then MS chromatograms are obtained for each
m/z 30(NO)
configuration where an product of oxidative dissociation. Since the dissociation
element-selective combustion unit is products are unique for each element contained in the
connected after the GC and before CxHyNzOw xCO2 + (y/2)H2O + zNO compound, a unique chromatogram is obtained for each
the MS. In this mode, specific hetero-element contained in the compound.
oxygen/nitrogen-containing
compounds can be selectively 18 O2 in Helium
detected. After separating
hydrocarbon compounds with GC, Principle of Detecting Oxygenated Compounds
the compounds are oxidatively
decomposed in the combustion In the analysis of oxygenated compounds, oxidative decomposition is performed using isotopic oxygen ( O2) in the
18
catalytic reactor and detected using GC-MS GC EL-30 carrier gas, and screening is conducted to separate oxygen-containing compounds from other components.
the SIM mode. Dedicated data analysis tools are employed to accurately identify oxygen-containing compounds.
MS Chromatogram from GC-Comb-MS 18 O2 (Isotopic) Oxidation Gas 16 O2 Oxidation Gas
After screening
4 Before screening (Oxygen Content Analysis)
2
16
16
16
18
18
16
16
16
+
11 14 CxHy O + 18 O2 C O2 + H2 O + C O2 H2 O CxHy O + 16 O2 C O2 + H2 O
5 10 1 Cyclohexanone 8 Hexylbutyrate m/z 44 18 48 20 m/z 44 18
6
1 3
7 8 2 2-ethoxyethylacetate 9 Dodecane
13
12 3 Benzaldehyde 10 Phenethyl acetate
9 Oxygen from Oxygen from Oxygen originating from oxygenated compounds cannot be
4 Dimethyl malonate 11 Dimethyl phthalate oxygenated compounds oxidation gas discriminated from oxygen originating from oxidation gas.
5 2-pentyl butyrate 12 Acephatene
6 Acetaldehyde 13 Dibenzofurane
7 1-octanol 14 Eicosane
CxHy
Note: This provides a unique chromatogram that can be used
to determine whether compounds contain oxygen. CxHyNz
Compounds 9, 12, and 14 do not contain oxygen. CxHyOz
Intensity C O2 Oxidation product of organic compounds
18
MS Direct Mode NO Origin of nitrogen-containing compounds
16
m/z C O2 Origin of oxygen-containing compounds
Retention Time
The MS Direct mode is a common configuration in GC-MS. The ELEM-SPOT system enables analysis in a typical GC-MS
setup without passing through the element-selective combustion unit by switching the configuration flow paths.
4 5