Page 7 - Shimadzu Journal vol.2 Issue4
P. 7
Forensics 107
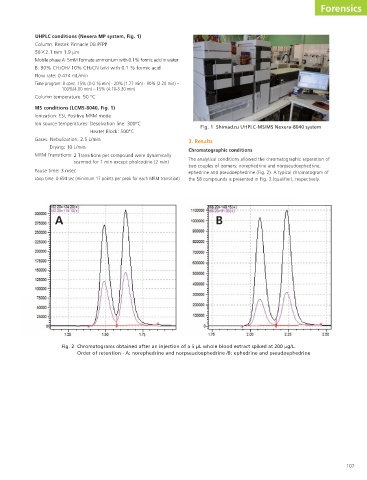
Fig. 1 Shimadzu UHPLC-MS/MS Nexera-8040 system
Chromatographic conditions The analytical conditions allowed the chromatographic separation of two couples of isomers: norephedrine and norpseudoephedrine; ephedrine and pseudoephedrine (Fig. 2). A typical chromatogram of the 58 compounds is presented in Fig. 3.(qualifier), respectively. B
3. Results Fig. 2 Chromatograms obtained after an injection of a 5 µL whole blood extract spiked at 200 µg/L. Order of retention - A: norephedrine and norpseudoephedrine /B: ephedrine and pseudoephedrine
UHPLC conditions (Nexera MP system, Fig. 1)
Column: Restek Pinnacle DB PFPP 50ʷ2.1 mm 1.9 µm Mobile phase A: 5mM Formate ammonium with 0.1% formic acid in water B: 90% CH3OH/ 10% CH3CN (v/v) with 0.1 % formic acid Flow rate: 0.474 mL/min Time program: B conc. 15% (0-0.16 min) - 20% (1.77 min) - 90% (2.20 min) – 100%(4.00 min) – 15% (4.10-5.30 min) Column temperature: 50 °C MS conditions (LCMS-8040, Fig. 1) Ionization: ESI, Positive MRM mode Ion source temperatures: Desolvation line: 300°C Heater Block: 500°C Gases: Nebulization: 2.5 L/min Drying: 10 L/min MRM Transitions: 2 Transitions per compound were dynamically scanned for 1 min except pholcodine (2 min) Pause time: 3 msec
Finally, 5 µL were injected in the UHPLC-MS/MS system. The whole
amphetamines, as well as cocaine and 4 of its metabolites) and 18
isotopically labeled internal standards (in order to improve method
µL of acetonitrile. After a 15 s shaking, the mixture was placed at
precision and accuracy) at 20 µg/L in acetonitrile (20 µL), and 200
sesquihydrate) were added and the mixture was shaken again for
15 s and centrifuged for 10 min at 12300 g. The upper layer was
diluted (1/3; v/v) with a 5 mM ammonium formate buffer (pH 3).
To 100 µL of sample (urine, whole blood or plasma) were added
-20°C for 10 min. Then approximately 50 mg of QuEChERS salts
isotopically labeled internal standards (designed with *) (Table1).
This method involves 40 compounds of interest (13 opiates, 22
-6-monoacetylmorphine* -Dextromethorphan -Dihydrocodeine* -Ethylmorphine -Hydrocodone -Hydromorphone -Methylmorphine* -Morphine* -Naloxone* -Naltrexone* -Noroxycodone* -Oxycodone* -Pholcodine
1 CHU Limoges, Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Unit of clinical and forensic toxicology, Limoges, France ;
*Part of this work was presented in a poster session of the 62 th ASMS Conference, 15 - 19 June, 2014, Baltimore.
Opiates
Sylvain DULAURENT 1 , Mikaël LEVI 2 , Jean-michel GAULIER 1 , Pierre MARQUET 1,3 and Stéphane MOREAU 2
2 Shimadzu France SAS, Le Luzard 2, Boulevard Salvador Allende, 77448 Marne la Vallée Cedex 2
plasma and urine by UHPLC-MS/MS using a QuEChERS sample preparation
2. Methods and Materials (MgSO4/NaCl/Sodium citrate dehydrate/Sodium citrate acquisition method lasted 5.5 min.
Determination of opiates, amphetamines and cocaine in whole blood,
Amphetamines or related compounds -2-CB -2-CI -4-MTA -Ritalinic acid -Amphetamine* -BDB -Ephedrine* -MBDB -m-CPP -MDA* -MDEA* -MDMA* -MDPV -Mephedrone -Metamphetamine* -Methcathinone -Methiopropamine -Methylphenidate -Norephedrine -Norfenfluramine -Norpseudoephedrine -Pseudoephedrine Table 1 list of analyzed compounds with their associate internal standard (*)
global w430×h280 3 Univ Limoges, Limoges, France 1. Introduction The determination of drugs of abuse (opiates, amphetamines, cocaine) in biological fluids is still an important issue in toxicology, in cases of driving under the influence of drugs (DUID) as well as in forensic toxicology. At the end of the 20th century, the analytical methods able to determine these three groups of narcotics were mainly based on a liquid-liquid-extraction with derivatization followed by GC-MS. Then LC-MS/MS was proposed, coupled with off-line sample preparation. Recently, on-line Solid-Phase-Extraction coupled with UHPLC-MS/MS was described, but in our hands it gave rise to significant carry-over after highly co
Forensics 106