Page 7 - Shimadzu Journal vol.7 Issue1
P. 7
Environmental Analysis
information about whether microplastics are being ingested by descends from the surface but it also inhabited by organisms well
abyssal or hadal organisms. This means that we still do not know adapted to a low food environment. Many deep-sea organisms,
whether microplastics are ingested by the organisms that live at including amphipods, exhibit high trophic plasticity and have
some of the deepest points in the ocean. evolved diverse morphological and physiological adaptations to
Given the range of transport pathways, the quantities produced ensure feeding success at rare opportunities, therefore in the
and released each year, plus the estimates of the volume currently presence of relatively new foreign bodies, the likelihood of
floating in the ocean, particularly in the large gyres, it is intuitive ingestion is high [52] .
that The objective of this study was to examine the extent of
the ultimate sink for this debris, in whatever size, is the deep microplastic and microfiber pollution across some of the deepest
sea . Plastics reaching the massive expanse of the deep sea are points of the ocean. Specifically, this study investigated the
[7]
ultimately contaminating an ecosystem we know far less about presence of ingested microplastic fibres and fragments in the hind
than the area from where it originates. This is especially the case gut of Lysianassoid amphipods across multiple hadal trenches
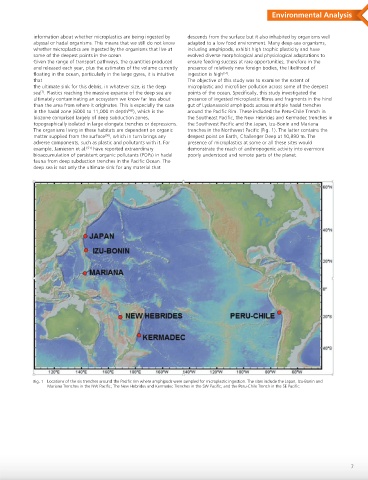
in the hadal zone (6000 to 11,000 m depth [43] ), which is the around the Pacific Rim. These included the Peru-Chile Trench in
biozone comprised largely of deep subduction zones, the Southeast Pacific, the New Hebrides and Kermadec trenches in
topographically isolated in large elongate trenches or depressions. the Southwest Pacific and the Japan, Izu-Bonin and Mariana
The organisms living in these habitats are dependent on organic trenches in the Northwest Pacific (Fig. 1). The latter contains the
matter supplied from the surface [50] , which in turn brings any deepest point on Earth, Challenger Deep at 10,890 m. The
adverse components, such as plastic and pollutants with it. For presence of microplastics at some or all these sites would
example, Jamieson et al. [51] have reported extraordinary demonstrate the reach of anthropogenic activity into evermore
bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in hadal poorly understood and remote parts of the planet.
fauna from deep subduction trenches in the Pacific Ocean. The
deep sea is not only the ultimate sink for any material that
Fig. 1 Locations of the six trenches around the Pacific rim where amphipods were sampled for microplastic ingestion. The sites include the Japan, Izu-Bonin and
Mariana Trenches in the NW Pacific; The New Hebrides and Kermadec Trenches in the SW Pacific; and the Peru-Chile Trench in the SE Pacific.
7