Page 14 - Shimadzu Journal vol.4 Issue1
P. 14
New Energy
C 30H 62
n-C 28H 58
ᶃ ʢI.S.ʣ
ᶄ
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
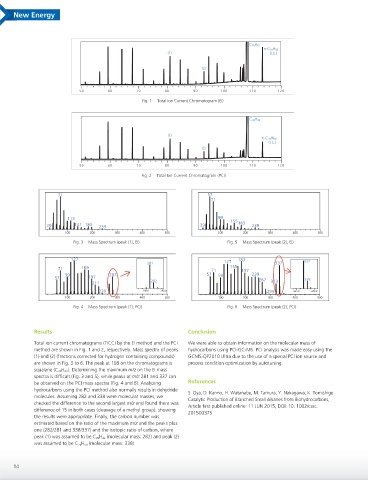
Fig. 1 Total Ion Current Chromatogram (EI)
C 30H 62
ᶃ
n-C 28H 58
ɹʢI.S.ʣ
ᶄ
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
Fig. 2 Total Ion Current Chromatogram (PCI)
71 57
71
113 99 155
29 141 183 239 29 183 239
100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500
Fig. 3 Mass Spectrum (peak (1), EI) Fig. 5 Mass Spectrum (peak (2), EI)
127 183 337
281 127 337
71 169 71 155 197
99 281 57 99 239
57 197 267 338
211 282 323
239 280.0 284.4 295 335.0 340.0
100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500
Fig. 4 Mass Spectrum (peak (1), PCI) Fig. 6 Mass Spectrum (peak (2), PCI)
Results Conclusion
Total ion current chromatograms (TICC) by the EI method and the PCI We were able to obtain information on the molecular mass of
method are shown in Fig. 1 and 2, respectively. Mass spectra of peaks hydrocarbons using PCI-GC-MS. PCI analysis was made easy using the
(1) and (2) (fractions corrected for hydrogen containing compounds) GCMS-QP2010 Ultra due to the use of a special PCI ion source and
are shown in Fig. 3 to 6. The peak at 108 on the chromatograms is process condition optimization by autotuning.
squalane (C 30 H 62 ). Determining the maximum m/z on the EI mass
spectra is difficult (Fig. 3 and 5), while peaks at m/z 281 and 337 can
be observed on the PCI mass spectra (Fig. 4 and 6). Analyzing References
hydrocarbons using the PCI method also normally results in dehydride
S. Oya, D. Kanno, H. Watanabe, M. Tamura, Y. Nakagawa, K. Tomishige
molecules. Assuming 282 and 338 were molecular masses, we
Catalytic Production of Branched Small Alkanes from Biohydrocarbons,
checked the difference to the second largest m/z and found there was
Article first published online: 11 JUN 2015, DOI: 10. 1002/cssc.
difference of 15 in both cases (cleavage of a methyl group), showing
201500375
the results were appropriate. Finally, the carbon number was
estimated based on the ratio of the maximum m/z and the peaks plus
one (282/281 and 338/337) and the isotopic ratio of carbon, where
peak (1) was assumed to be C 20 H 42 (molecular mass: 282) and peak (2)
was assumed to be C 24 H 50 (molecular mass: 338).
14