
The TOC-L series of TOC analyzers adopts the 680°C combustion catalytic oxidation method, which was developed by Shimadzu and is now used worldwide. While providing an ultra wide range of 4 μg/L to 30,000 mg/L, these analyzers boast a detection limit of 4 μg/L through coordination with NDIR. This is the highest level of detection sensitivity available with the combustion catalytic oxidation method. In addition, the combustion catalytic oxidation method makes it possible to efficiently oxidize not only easily-decomposed, low-molecular-weight organic compounds, but also hard-to-decompose insoluble and macromolecular organic compounds.
Extremely wide measurement range from 4 μg/L to 30,000 mg/L, applicable to everything from ultrapure water to highly contaminated water (TOC-LCSH/CPH)
- Capable of TC, IC, TOC (= TC-IC), and NPOC measurement; options enable POC (volatile organic carbon), TOC via POC + NPOC, and even TN (total nitrogen) measurements
- The blank check function evaluates system blanks by measuring ultrapure water processed automatically within the instrument
- The automatic dilution function enables measurements up to 30,000 mg/L
Reliable sample injection system
- Automatic sample acidification and sparging
- The automatic dilution function reduces sample salinity, acidity, and alkalinity, significantly extending the period of use of catalysts and combustion tubes (The period of use depends on the sample and measurement conditions.)
- Stat or priority samples can be added at anytime to the analysis schedule without interrupting operation even when an autosampler is used
Select from 4 models to suit your application

The TOC-L series consists of a high-sensitivity model with a detection limit of 4 μg/L, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including pure water measurements, and a standard model designed with cost performance in mind. Each analyzer is available as an LCD and keyboard-equipped standalone model, or as a PC-controlled model.
In addition, the USB format has been adopted as the external interface, enhancing the equipment’s versatility. Even the standalone models are capable of output to a general-purpose PC printer or to a USB memory stick.
Options to further enhance functionality
With the TOC-L series, numerous options enable a variety of functional enhancements. These include simultaneous measurement of TOC and TN (total nitrogen) (when a TN unit is added), the use of compressor air (when a carrier gas purification kit is added), and the measurement of gas samples and solid samples (when a gas sample injection kit and solid sample combustion unit are added).
Sea water sample measurement and small sample volume options have also been enhanced.
Space-saving and energy-saving design
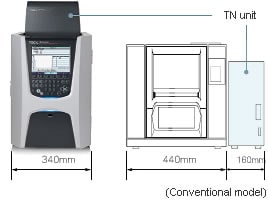
The width of the instrument is 20 % less in comparison with conventional Shimadzu models. This enables more effective use of laboratory space. The instrument width is unchanged even when the TN unit is added.

This product conforms with Shimadzu’s ECO labeled product. Energy Saving: Power consumption reduced by 36 % (100 V) and 43 % (200 V) as compared to a conventional Shimadzu product. (Assuming 8 hours operation/day × 5 days/week)
Find Out the Optimal TOC Analyzer
Explore which TOC Analyzer system is ideal for your samples and applications by answering a few questions. Click the botton below to get started.
680°C Combustion Catalytic Oxidation Method
Developed by Shimadzu, the 680°C combustion catalytic oxidation method is now used worldwide. One of its most important features is the capacity to efficiently oxidize hard-to-decompose organic compounds, including insoluble and macromolecular organic compounds.
TOC (total organic carbon) Measurement
The 680°C combustion catalytic oxidation method achieves total combustion of samples by heating them to 680°C in an oxygen-rich environment inside TC combustion tubes filled with a platinum catalyst. Since this utilizes the simple principle of oxidation through heating and combustion, pretreatment and post-treatment using oxidizing agents are unnecessary, which enhances operability. The carbon dioxide generated by oxidation is detected using an infrared gas analyzer (NDIR). By adopting a newly-designed, high-sensitivity NDIR, the TOC-L series achieves high detection sensitivity, with a detection limit of 4μg/L, the highest level for the combustion catalytic oxidation method. The figure below is a schematic diagram showing TOC measurement using the 680°C combustion catalytic oxidation method and the NDIR method.
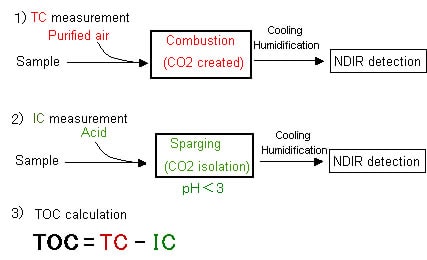
The sample is delivered to the combustion furnace, which is supplied with purified air. There, it undergoes combustion through heating to 680°C with a platinum catalyst. It decomposes and is converted to carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide generated is cooled and dehumidified, and then detected by the NDIR. The concentration of TC (total carbon) in the sample is obtained through comparison with a calibration curve formula. 1) Furthermore, by subjecting the oxidized sample to the sparging process, the IC (inorganic carbon) in the sample is converted to carbon dioxide, and the IC concentration is obtained by detecting this with the NDIR. 2) The TOC concentration is then calculated by subtracting the IC concentration from the obtained TC concentration. 3)
NPOC (non-purgeable organic carbon) Measurement
In environmental water and other samples in which the IC component of the TC is extremely large, significant errors may result if the abovementioned method is used for TOC measurement. Accordingly, the organic carbon in the sample is usually measured via an NPOC measurement as shown in the figure below. This method is the same as TOC measurement methods using acidification and sparging (IC removal) as described in official measurement methods (such as JIS and ASTM).
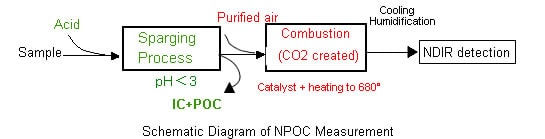
By sparging samples to which a small amount of acid has been added, the IC in the sample is converted to carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide is removed, and the TOC is obtained by measuring the TC in the treated sample. When the carbon dioxide from the IC is removed, POC (purgeable organic carbon) may also be lost. Accordingly, the TOC obtained with this method may be referred to as NPOC. Shimadzu provides options that measure this POC, which is typically lost, enabling more complete TOC measurement.
Software Features Intuitive Operability and a Wealth of Functions
LabSolutions™ TOC PC Software Enabling Simple, Intuitive Operation



