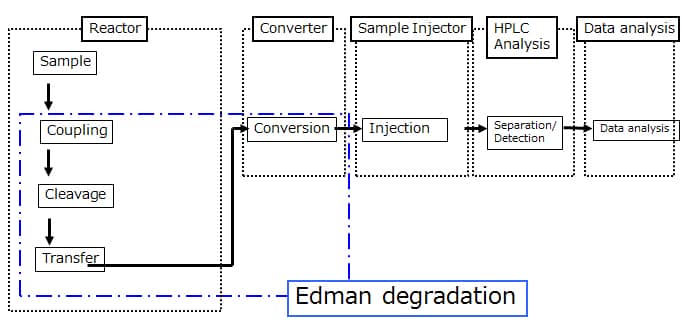
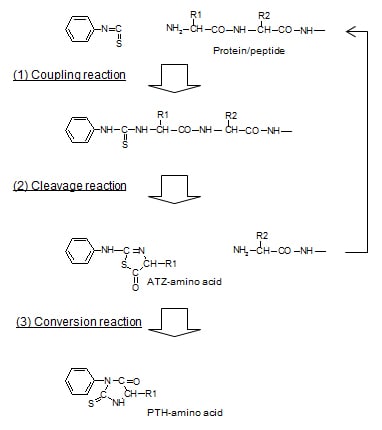
The PPSQ is an instrument for determining the amino acid sequences of proteins and peptides, which combines an Edman reaction section with a high performance liquid chromatograph (HPLC). There are 2 types: the PPSQ-51A, which is equipped with one reactor, and the PPSQ-53A, which is equipped with three reactors. On the PPSQ-53A, the continuous analysis of the amino acid sequences of multiple samples can be performed one after another. In the Edman reaction section, amino acids are cleaved in order from the N-terminal of a protein by repeatedly performing Edman degradation, and are derivatized. As a result, stable PTH-amino acids are produced. The PTH-amino acids are injected online into the HPLC, and analysis is performed. The HPLC data is saved on the PC, and data processing software is used to process the chromatograms. Then, amino acid sequence estimation software is used to identify the amino acids and estimate the sequences.

Isocratic System

Gradient System
Benefits of using Edman degradation for amino acid sequencing
(1) Guaranteed N-terminal sequence of proteins
(2) No sample pre-treatment required
(3) Differentiation of isobaric amino acids (leucine and isoleucine)
(4) Identification possible even from unknown proteins not registered in databases
Compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11
LabSolutions PPSQ software provides compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 guidelines and enables compliance with the security, user management, and audit trail requirements specified by FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
1. Security
Users are managed on the basis of groups, with each user being recognized by means of a username and password. Unique groups can be created by including persons having different access privileges. Clearly defining each user’s access privileges prevents unauthorized changes to settings, instrument operation, and data access.
2. User Management
LabSolutions’ user administration comprises the setting of rights groups and assignment of rights to users just as in Windows. Access rights required for each user can be set by assigning various levels of access to each user. This helps achieve effective user administration and more efficient laboratory operations.
3. Audit Trail
Logins and logouts to the system, changes in users and groups, and the start and completion of acquisition, together with the username and the time, are all recorded. The recorded operational log can be registered in the database to provide traceability.
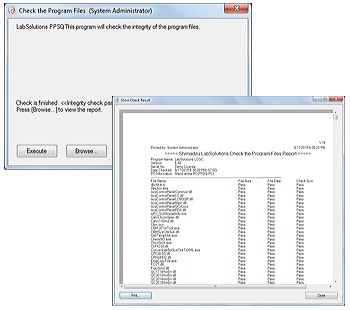
4. Software Validation
The integrity of the programs that comprise the system and the raw data acquired by instruments can be checked, ensuring the reliability of the system and data. The results of these alteration checks can be managed as printouts.
(Include Fig)
Simple, Easy-to-Use Data Analysis Functions
Specialized protein sequencer software makes it simple to perform the reprocessing of chromatograms, the overlay of multiple chromatograms, and the automatic estimation of amino acid sequences, which are required for sequence analysis.
- Reprocessing of chromatograms required for data analysis
- Overlay of multiple chromatograms
- Automatic estimation of amino acid sequences
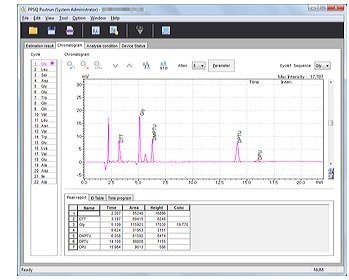
- Chromatogram peak integration, printing, and other processes can be performed on a per-sample basis.
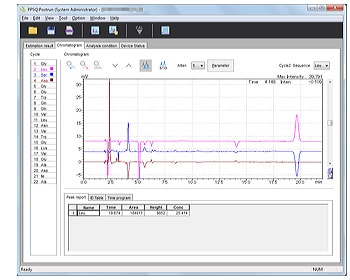
- Displays multiple chromatograms. Analysis cycles can be updated simply by clicking a button.
- Window allows easy identification of sequences.
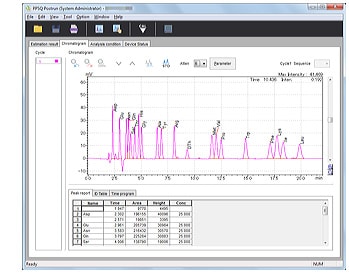
- Calibrates PTH-amino acid retention times.
- Retention times can be edited simply by selecting a PTH-amino acid and clicking a peak.
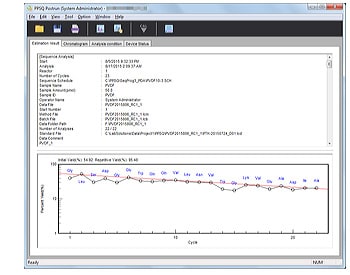
- Automatically generates a report containing analytical parameters, estimated sequences, yield rates, and other information.
Automatic Sequence Estimation
Sequences are automatically estimated after analysis of each cycle is complete. Up to four candidate amino acids are displayed together with their certainty levels.
Customized Reports
Reports containing information such as analytical parameters, estimated sequences, and yield rates are automatically created.
Yield Graph Display
Initial and repeated yield rates are calculated and displayed in graph form. Amino acids used for calculations can be freely selected.
Structure
Using Edman degradation, it derivatizes the amino acids of a protein in order from the N-termini, cleaves the derivatives, and from the HPLC retention times for these cleaved derivatives, identifies the amino acids.
Isocratic System
Baseline Stability
PPSQ series protein sequencers separate PTH-amino acids isocratically. This improves baseline stability and allows high-sensitivity analysis of PTH-amino acids.
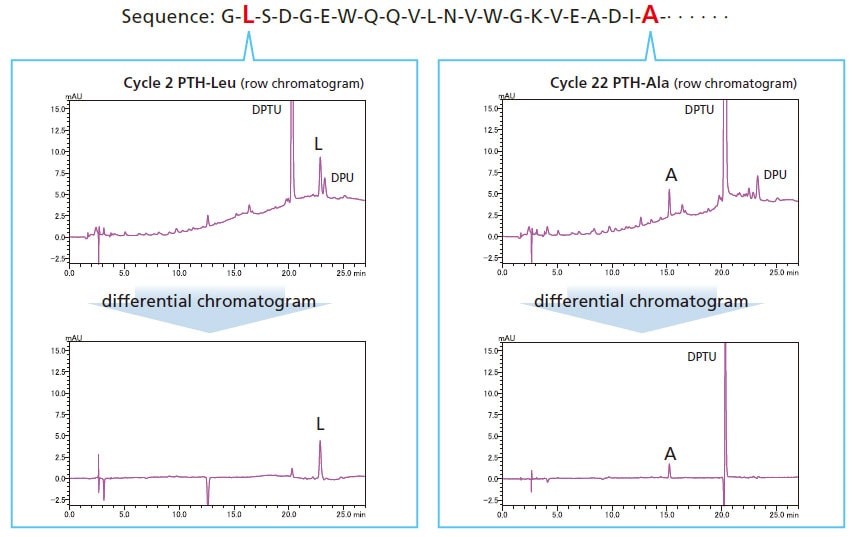
Retention Time Reproducibility
Isocratic sequence analysis provides more stable retention times. Therefore, peaks detected in previous cycles can be cancelled using substation chromatogram processing, making it easier to identify sequences.
Higher Detection
Cycle 10 PTH-Val
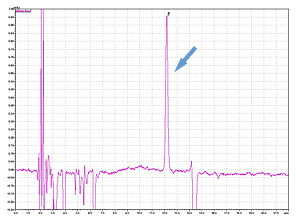
PPSQ-51A/53A
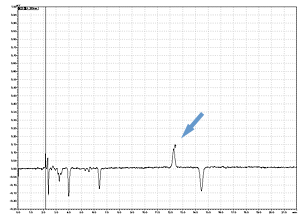
PPSQ-31B/33B
Cycle 21 PTH-Ile
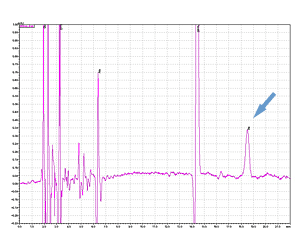
PPSQ-51A/53A
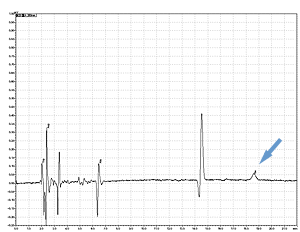
PPSQ-31B/33B
Sample: Horse myoglobin 10pmol
Results show the subtraction chromatograms by SPD-M30A (PPSQ-51A/53A) and SPD-20A (PPSQ-31B/33B) connected tandemly after Edman degradation.
Environmentally friendly eco-design
Performing PTH-amino acid analysis in an isocratic mode in which eluents are recycled to allow repeated use of the mobile phase makes it possible to reduce liquid waste and running costs.
Gradient System
High-Sensitivity Analysis
A high-sensitivity flow cell enables high-sensitivity detection of PTH-amino acids, which allows for sequential analysis using trace samples.
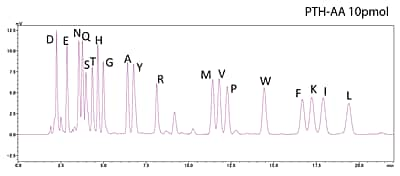
Analysis of Standard PTH-Amino Acid Mixture
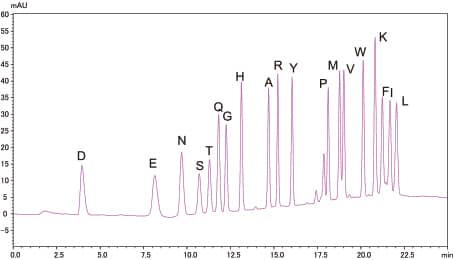
10pmol
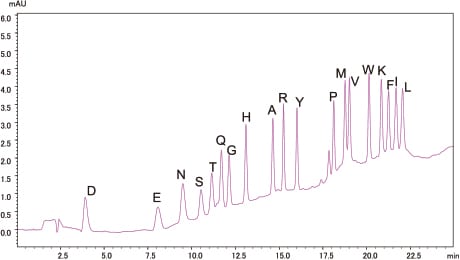
500fmol
Analysis Stability
This system has high analysis stability because it is equipped with a high-performance detector and a solvent delivery pump that provides excellent pumping performance, even in the micro flowrate range, combine to ensure high analysis stability. Because chromatograms with good reproducibility can be obtained, peaks detected in the previous cycle can be canceled by performing differential chromatogram processing. This enables easy identification of PTH-amino acids even from trace samples.
Analysis of Horse Myoglobin (10 pmol)