Page 7 - Cannabis&Hemp Cannabis Testing Solution
P. 7
Potency Testing Alternatives
SFC Analysis
HPLC has long been considered the gold standard for the quantitative analysis of cannabinoids in cannabis and
hemp growing for its robust methods, efficacy for both acid and neutral forms, and its simple sample preparation.
A lesser known technique is supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) which uses supercritical CO as the primary
2
mobile phase.
SFC offers advantages over HPLC. First, the use of CO
2
allows for increased flow rates due to the lower viscosity
and backpressure compared to aqueous solvents. In
addition, SFC is generally regarded as a “green” technique
due to the minimization of organic solvents and reduced
generation of hazardous waste. This has the added
advantage of reducing the operating cost of the instrument
as far less hazardous waste is produced. For the full
application, request Shimadzu’s Application News No.
HPLC-034 for analysis of 9 cannabinoids.
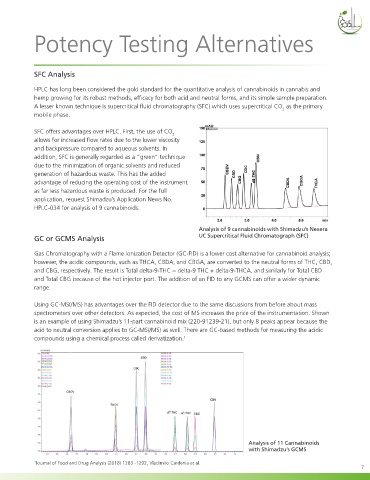
Analysis of 9 cannabinoids with Shimadzu’s Nexera
GC or GCMS Analysis UC Supercritical Fluid Chromatograph (SFC)
Gas Chromatography with a Flame Ionization Detector (GC-FID) is a lower cost alternative for cannabinoid analysis;
however, the acidic compounds, such as THCA, CBDA, and CBGA, are converted to the neutral forms of THC, CBD,
and CBG, respectively. The result is Total delta-9-THC = delta-9 THC + delta-9-THCA, and similarly for Total CBD
and Total CBG because of the hot injector port. The addition of an FID to any GCMS can offer a wider dynamic
range.
Using GC-MS(/MS) has advantages over the FID detector due to the same discussions from before about mass
spectrometers over other detectors. As expected, the cost of MS increases the price of the instrumentation. Shown
is an example of using Shimadzu’s 11-part cannabinoid mix (220-91239-21), but only 8 peaks appear because the
acid to neutral conversion applies to GC-MS(/MS) as well. There are GC-based methods for measuring the acidic
compounds using a chemical process called derivatization. 1
Analysis of 11 Cannabinoids
with Shimadzu’s GCMS
1 Journal of Food and Drug Analysis (2018) 1283 -1292, Vladimiro Cardenia et al.
7